Imagine you could have a clear visual of scabies when they emerge from their lurking spots. Picture small, itchy bumps on the skin, resembling rashes or insect bites. Their appearance may vary from person to person, but one thing is certain – these tiny parasites can cause quite a stir when they make their presence known. In this article, we will explore the distinct characteristics of scabies and shed light on what exactly they look like when they come out, giving you a clearer understanding of this common yet troublesome skin condition.
Appearance of Scabies
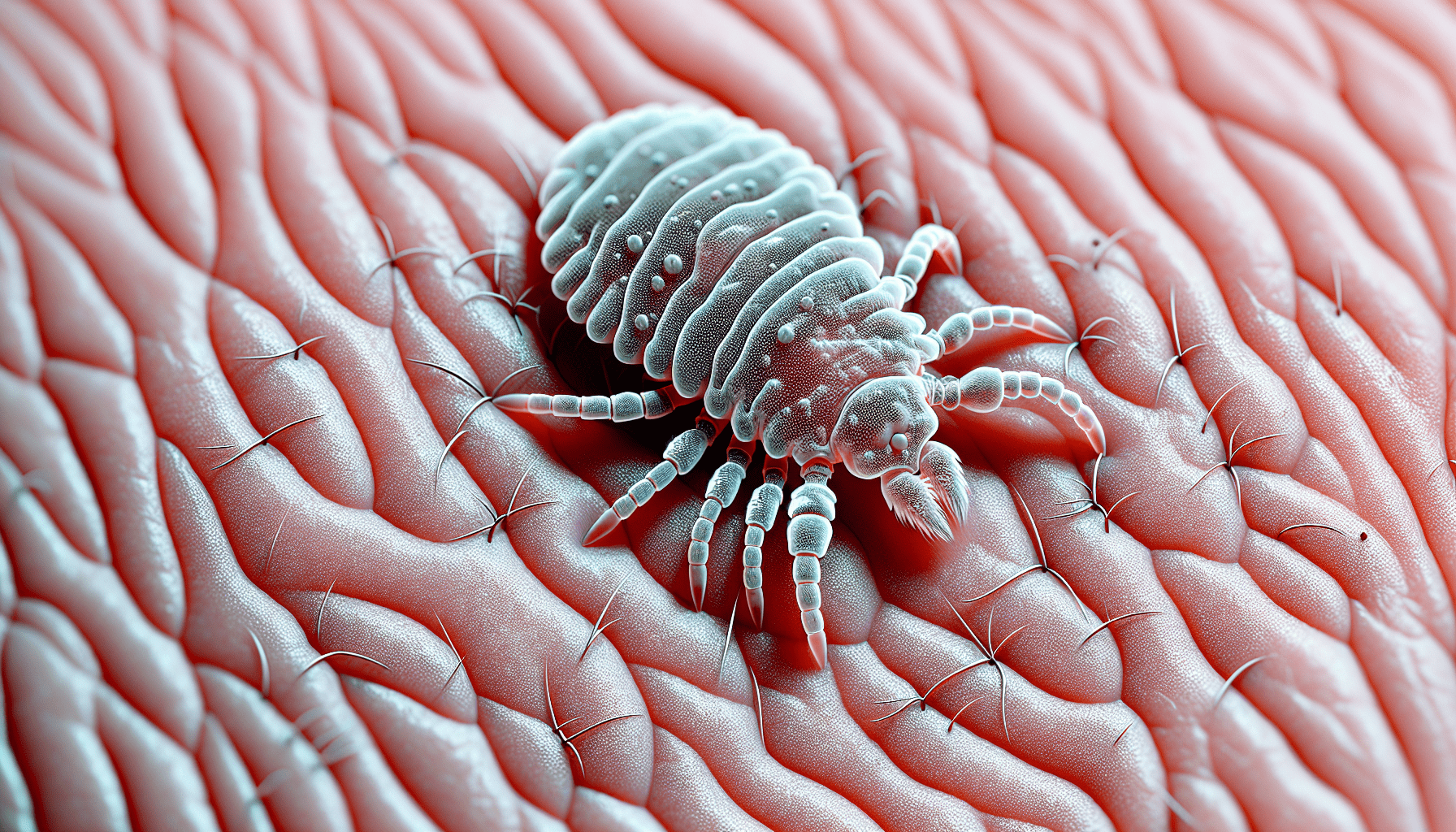
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by tiny mites known as Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites are microscopic and can barely be seen with the naked eye. However, they do have certain characteristics that can help identify them.
Characteristics of Scabies Mites
Scabies mites are approximately 0.2 to 0.4 millimeters in length, making them barely visible to the human eye. They have an oval-shaped body with eight legs and are equipped with tiny mouthparts for burrowing into the skin. These mites are considered to be ectoparasites as they live on the surface of the skin.
Size and Shape
Despite being minuscule, scabies mites are noticeable under a magnifying glass or microscope. Their size is comparable to the point of a needle, and their oval-shaped bodies allow them to easily navigate through the skin’s outer layer.
Color and Texture
Scabies mites often have a translucent or greyish appearance, making them blend in with the color of the skin. Their bodies have a slightly rough texture, which aids in their ability to burrow beneath the skin’s surface.
Visible Signs of Scabies Infestation
Scabies infestation can cause a range of visible signs on the skin. These signs may vary from person to person, but there are some common indicators of scabies.
Burrows on the Skin
One of the most distinctive signs of a scabies infestation is the presence of burrows on the skin. These burrows appear as thin, raised, and winding lines that are often accompanied by a small dark dot at one end. The burrows are created by the female mites as they tunnel into the skin to lay their eggs.
Rash and Redness
Scabies mites provoke an immune response in the skin, leading to the development of a rash. The rash is typically itchy and can appear as small red bumps or patches on the affected areas. It may be more pronounced in areas where the mites have burrowed into the skin.
Intense Itching
One of the most distressing symptoms of scabies is intense itching, which tends to worsen at night. The itching is a result of the body’s allergic reaction to the mites and their fecal matter. Scratching can further exacerbate the itching and may cause complications like open sores or skin infections.
Pimple-Like Bumps
Scabies infestation may also lead to the formation of pimple-like bumps on the skin. These bumps, known as papules, are usually small, red, and raised. They can occur in clusters and are often accompanied by itching and inflammation.
Scabies in Different Body Parts
Scabies infestation can occur on various parts of the body, and the location of the infestation can affect the appearance and symptoms.
Face and Scalp
While scabies is more commonly found in areas with skin folds and creases, it can also affect the face and scalp. In these areas, scabies may cause a rash, intense itching, and tiny red bumps. It is important to be cautious when using scabicide creams on the face and scalp due to their sensitivity.
Hands and Wrists
The hands and wrists are common sites for scabies infestation, particularly among adults. The burrows may be more visible in these areas due to the thinner skin. Itching and small bumps can be expected.
Genital Area
Scabies can also affect the genital area, causing intense itching, a rash, and red bumps. It is essential to seek medical attention if scabies is suspected in this region, as it can be mistaken for other conditions, such as a sexually transmitted infection.
Armpits and Elbows
In the armpits and elbow creases, scabies mites may cause itching, redness, and the formation of papules. These areas are prone to friction and sweat, making them attractive spots for mite infestation.
Feet and Ankles
The feet and ankles are commonly affected by scabies, especially in children and older adults. The burrows and associated rash may be more visible in these areas due to the thinner skin. Itching and redness are common symptoms.
Scabies Symptoms in Children
Children are particularly prone to scabies infestations, and the symptoms can manifest differently than in adults.
Crusts and Pustules
In severe cases of scabies infestation in children, crusts and pustules may develop. These lesions can be blister-like and fluid-filled, and they often occur in between fingers or on the palms and soles of the feet. Crusts and pustules can lead to discomfort and pain, requiring prompt medical attention.
Sores and Secondary Infections
Repeated scratching of the itchy skin caused by scabies can lead to open sores. These sores increase the risk of secondary infections, such as impetigo. It is crucial to keep the affected areas clean and prevent scratching to minimize the chances of complications.
Scabies vs Other Skin Conditions
Scabies shares some similarities with other skin conditions, and it is important to differentiate between them for proper treatment and management.
Scabies vs Bed Bugs
While both scabies and bed bug infestations can cause skin rashes and itching, there are subtle differences that can help distinguish between the two. Scabies rashes generally appear as small red bumps and may have visible burrows, whereas bed bug bites are often in a line or cluster and may appear as larger welts.
Scabies vs Eczema
Eczema is a chronic inflammation of the skin that can cause red, itchy, and scaly patches. Unlike scabies, eczema is not caused by mites and does not involve burrows. Eczema tends to be more persistent and may appear in areas not typically affected by scabies, such as the back of knees or inside elbows.
Scabies vs Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are characterized by raised, itchy welts on the skin. Unlike scabies, hives are typically caused by an allergic reaction and are not the result of a mite infestation. Hives can appear and disappear rapidly and often do not leave any lasting marks on the skin.
How to Confirm Scabies?
If you suspect a scabies infestation, it is essential to seek confirmation from a healthcare professional. They can help diagnose scabies through various means.
Seeking Medical Diagnosis
A healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination of the affected areas to look for signs of scabies, such as burrows, rash, or red bumps. They may also inquire about your symptoms and medical history to make an accurate diagnosis.
Scabies Tests
In some cases, the healthcare professional may perform additional tests to confirm the presence of scabies mites. These tests may include skin scrapings, where a small sample of the affected skin is collected and examined under a microscope to detect the mites or their eggs.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Once a scabies infestation is confirmed, treatment is necessary to eliminate the mites and alleviate symptoms.
Topical Medications
The most common form of treatment for scabies is the application of topical medications. These medications, known as scabicides, contain ingredients that effectively kill the mites and their eggs. Permethrin and sulfur-based creams are commonly prescribed scabicides.
Oral Medications
In more severe cases of scabies, oral medications may be prescribed. These medications contain ingredients that help kill the mites from within the body, providing a comprehensive treatment approach. Oral ivermectin is a commonly used medication for scabies.
Environmental Cleaning
To prevent reinfestation and ensure the complete eradication of scabies mites, it is crucial to clean your environment. This includes washing all bedding, clothing, and towels in hot water and drying them on high heat. Vacuuming upholstered furniture and carpets can also help remove any mites or eggs that may be present.
Preventing Scabies Infestation
Prevention is key in avoiding a scabies infestation, especially in high-risk situations.
Avoiding Skin-to-Skin Contact
Scabies is typically spread through prolonged, direct skin-to-skin contact. To reduce the risk of infestation, it is advisable to avoid close contact with individuals who are known to have scabies or to take precautions like wearing protective clothing or gloves when in close proximity.
Washing and Laundering
Regularly washing your hands and body with soap and warm water can help reduce the chances of contracting scabies. Additionally, washing your clothes, bedding, and towels regularly with hot water and drying them on high heat can eliminate any potential mites or eggs.
Avoiding Sharing Personal Items
Since scabies mites can survive for a short period on personal items such as towels, bedding, or clothing, it is important to avoid sharing these items, especially in close quarters like dormitories or households. Keeping personal items separate can significantly reduce the risk of transmission.
In conclusion, while scabies mites may be difficult to see with the naked eye, their presence can be identified through visible signs such as burrows, rashes, intense itching, and pimple-like bumps. Scabies can appear on various body parts, and the symptoms may differ in children. It is important to differentiate scabies from other skin conditions for effective treatment. Seeking medical diagnosis and following prescribed treatment options are crucial steps in overcoming a scabies infestation. By practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact or sharing personal items, the risk of scabies can be minimized.