Have you ever experienced an itchy rash that just won’t go away? Well, there’s a possibility that it might not be scabies after all. In this article, we will explore the various conditions that can mimic scabies and share some valuable insights on how to differentiate between them. It’s time to unravel the mystery and put an end to that incessant itch!
Insect Bites
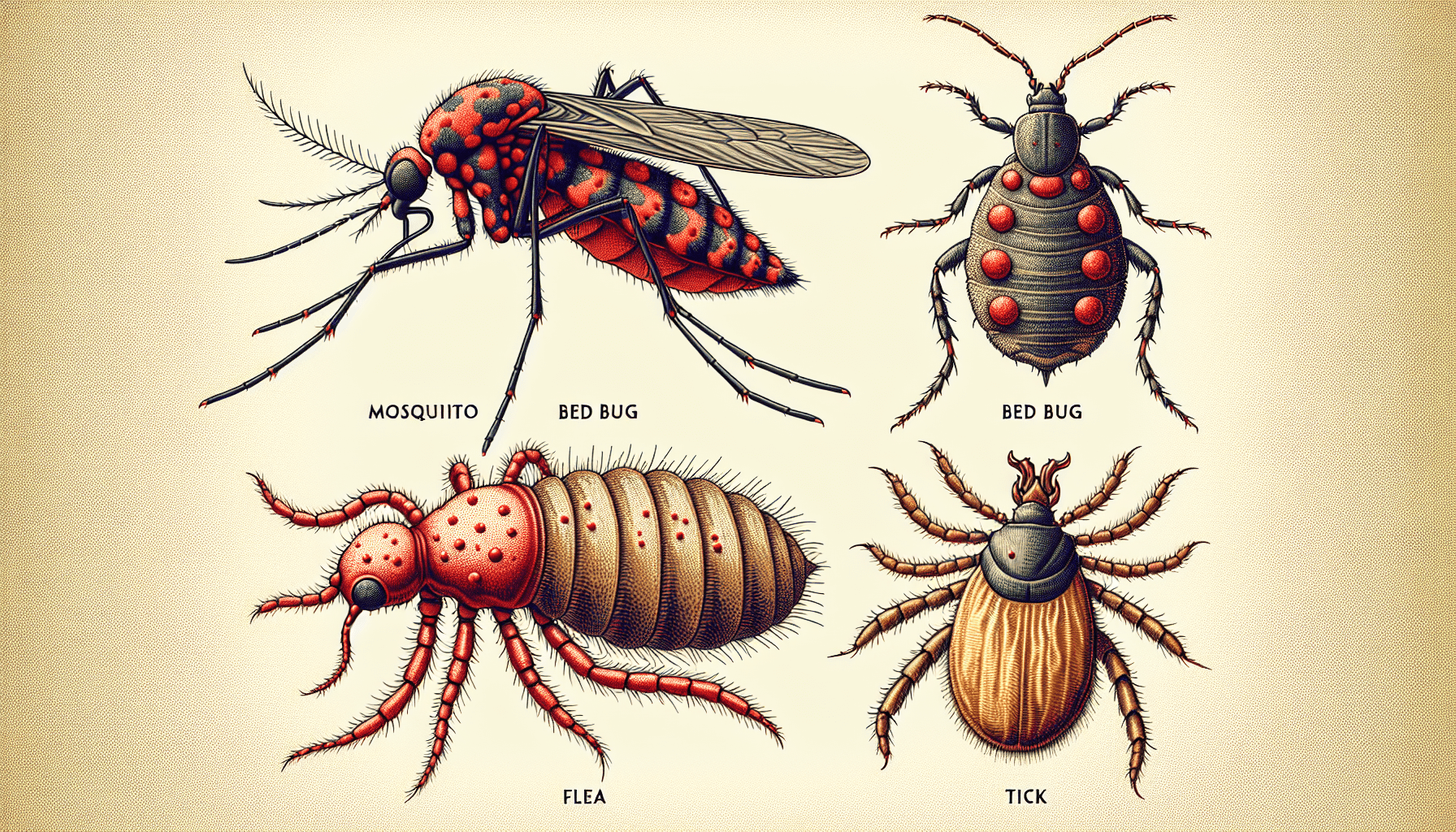
When it comes to insect bites, there are several common culprits that can leave you itching and irritated. Mosquito bites are perhaps the most well-known, with their characteristic red bumps and intense itching. Bed bug bites can also cause discomfort, often appearing as small red welts that may be grouped together. Flea bites, usually found on the lower legs and ankles, are another common annoyance. Finally, tick bites can be a concern, as they can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease. It’s important to be aware of these insects and take precautions to avoid their bites.
Mosquito Bites
Mosquitoes are a familiar annoyance, especially during the warmer months. They are attracted to human blood and leave behind itchy, red bumps when they bite. These bites can be particularly bothersome for some individuals, causing itching and swelling that can last for days. To protect yourself from mosquito bites, it’s important to wear long sleeves and pants when spending time outdoors, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active. Applying insect repellent containing DEET can also provide effective protection.
Bed Bug Bites
Bed bugs are small insects that feed on human blood while we sleep, often leaving behind itchy red welts on the skin. Although their bites are not known to transmit diseases, they can cause significant discomfort and distress. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, it’s important to thoroughly clean and vacuum your living spaces, wash bedding and clothing in hot water, and consider seeking professional pest control services to eliminate these unwelcome pests.
Flea Bites
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that infest pets and can also bite humans. Their bites are usually found on the lower legs and ankles, appearing as small red bumps surrounded by a reddish halo. Flea bites can cause intense itching and, in some cases, an allergic reaction. If you have pets, it’s important to regularly treat them for fleas and keep their living areas clean to prevent infestations. Additionally, maintaining good personal hygiene and wearing protective clothing can help reduce the risk of flea bites.
Tick Bites
Ticks are known for transmitting diseases such as Lyme disease, making their bites a cause for concern. These small arachnids latch onto the skin and feed on blood, often remaining attached for several days. Tick bites can result in a red, swollen area on the skin and may also cause flu-like symptoms. If you find a tick attached to your skin, it’s important to carefully remove it with tweezers, making sure to grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible. Seek medical attention if you experience any unusual symptoms or if the tick cannot be safely removed.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis refers to skin inflammation that occurs when the skin comes into contact with an allergen or irritant. This condition can cause redness, itching, and a rash. There are two main types of contact dermatitis: allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin develops an allergic reaction to a specific substance, such as certain metals, fragrances, or latex. The immune system mistakenly identifies these substances as harmful, triggering an allergic response. Common symptoms include red, itchy, and swollen skin at the site of contact. To manage allergic contact dermatitis, it’s important to identify and avoid the triggering substance. Topical corticosteroids and antihistamines may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is caused by direct damage to the skin from exposure to irritating substances, such as harsh chemicals or soaps. Unlike allergic contact dermatitis, this type of dermatitis does not involve an allergic reaction. Symptoms may include dry, red, and cracked skin that feels irritated and sore. To prevent irritant contact dermatitis, it’s important to minimize contact with irritants and use protective measures, such as wearing gloves, when handling chemicals. Moisturizing the skin regularly can also help maintain its protective barrier.
Eczema
Eczema is a chronic condition characterized by inflamed, itchy skin. It can be divided into several types, including atopic dermatitis, nummular eczema, and seborrheic dermatitis. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema and often begins in childhood. It is characterized by dry, itchy skin, red patches, and small bumps. These symptoms can vary in severity and may be triggered by allergens, stress, or irritants. Treatment for atopic dermatitis typically involves moisturizing the skin, avoiding triggers, and using topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators to reduce inflammation.
Nummular Eczema
Nummular eczema, also known as discoid eczema, is characterized by coin-shaped patches of inflamed skin. The patches can be itchy, red, and scaly, and may appear on the arms, legs, or torso. Nummular eczema is often triggered by dry skin, cold weather, or irritants. Treatment may involve keeping the skin moisturized, avoiding triggers, and using topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors to reduce inflammation.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common form of eczema that primarily affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It is characterized by red, scaly patches that can be itchy and greasy. Seborrheic dermatitis may be triggered by hormones, stress, or certain yeast overgrowth on the skin. Treatment typically involves using medicated shampoos or creams containing antifungal agents or corticosteroids to manage symptoms.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, silvery scales and itchy, dry patches. There are several types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and inverse psoriasis.
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most common form and is characterized by raised, red patches covered with silver-white scales. The patches can be itchy and may occur anywhere on the body, but are commonly found on the scalp, elbows, and knees. Treatment for plaque psoriasis may involve topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, or systemic medications to control inflammation and promote skin cell turnover.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, red, scaly spots that resemble water droplets. It often occurs suddenly and is commonly triggered by a bacterial or viral infection, such as strep throat. Guttate psoriasis typically resolves on its own within a few weeks to months, but treatment may involve topical corticosteroids or phototherapy to relieve symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis appears as smooth, red patches of inflamed skin that may be found in skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, or under the breasts. It can cause discomfort due to friction and sweat accumulation in these areas. Treatment for inverse psoriasis may involve topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, or phototherapy to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
Scabies Look-Alikes
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. However, there are other conditions that can mimic the symptoms of scabies. These include pediculosis, herpes simplex virus, pemphigus, and pityriasis rosea.
Pediculosis
Pediculosis, commonly known as lice infestation, can lead to intense itching and cause small red bumps or sores on the skin. Lice are tiny insects that infest the hair and scalp, feeding on blood. Treatment for pediculosis involves using medicated shampoos or lotions specifically designed to kill lice and their eggs, as well as thorough combing to remove any remaining lice.
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) can cause a variety of skin symptoms, including blister-like sores that can be mistaken for scabies. HSV infection is typically characterized by painful, fluid-filled blisters that can erupt and form crusts. Antiviral medications can help manage HSV outbreaks and reduce symptoms.
Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a group of rare autoimmune disorders that cause painful blistering of the skin and mucous membranes. These blisters can be similar in appearance to the lesions caused by scabies. Pemphigus requires medical diagnosis and treatment, usually with oral corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications.
Pityriasis Rosea
Pityriasis rosea is a common skin condition characterized by scaly, pink or red patches that often start with a larger “herald patch” followed by smaller patches appearing elsewhere on the body. The rash can resemble the burrows and nodules caused by scabies, leading to confusion. Pityriasis rosea usually resolves on its own within a few weeks to months, without specific treatment.
Drug Reactions
Some medications can cause adverse reactions in the skin, resulting in various skin conditions. Two severe drug reactions that can affect the skin are Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN).
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a rare but serious disorder that typically begins with flu-like symptoms, followed by the development of a widespread rash and the detachment of the top layer of skin. It can be triggered by certain medications, infections, or other underlying conditions. SJS is a medical emergency that should be treated in a hospital setting, with supportive care, withdrawal of the causative drug, and specialized wound care.
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a severe and life-threatening condition characterized by widespread skin detachment, similar to SJS but involving a larger body surface area. It is often caused by adverse drug reactions, with symptoms including fever, blistering, and sloughing of the skin. Treatment for TEN is similar to that of SJS, with intensive care support, withdrawal of the offending drug, and management of complications.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections of the skin, also known as dermatophytosis or ringworm, can cause itching, redness, and a characteristic ring-shaped rash. Several types of fungal infections can affect the skin, including tinea corporis, tinea versicolor, and candidiasis.
Tinea Corporis
Tinea corporis, commonly known as ringworm, is a fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body, most commonly the arms, legs, and trunk. It presents as a red, scaly rash with a well-defined border that may resemble a ring. Topical antifungal medications or oral antifungal drugs may be prescribed to treat tinea corporis and alleviate symptoms.
Tinea Versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a common fungal infection that primarily affects areas of the skin that tend to be oily, such as the chest, back, and upper arms. It causes patches of discolored skin, usually lighter or darker than the surrounding skin, resulting in a blotchy appearance. Treatment typically involves the use of antifungal shampoos, creams, or oral medications to control the fungal overgrowth.
Candidiasis
Candidiasis, also known as a yeast infection, is caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungus. It commonly affects moist areas of the body, such as the mouth, genitals, and skin folds. Symptoms may include red, itchy skin with a rash or small pustules. Topical antifungal creams or oral antifungal medications may be prescribed to treat candidiasis and relieve symptoms.
Scalp Conditions
The scalp is prone to various conditions that can affect the health and appearance of the hair and scalp. Common scalp conditions include head lice, dandruff, and seborrheic dermatitis.
Head Lice
Head lice infestations are a common problem, especially among children. These tiny insects attach themselves to the scalp and hair, causing intense itching and irritation. Treatment for head lice typically involves using over-the-counter or prescription medicated shampoos or lotions, along with thorough combing to remove lice and their eggs.
Dandruff
Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterized by the shedding of dead skin cells from the scalp. It can result in a flaky scalp, itchiness, and visible white flakes on the hair and clothing. Dandruff is often caused by an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia. Treatment usually involves using specialized dandruff shampoos containing ingredients like coal tar, zinc pyrithione, or selenium sulfide to control the yeast and reduce flaking.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic scalp condition that causes red, greasy, and scaly patches on the scalp. It can also affect other areas rich in oil glands, such as the face and chest. Seborrheic dermatitis may be triggered by hormones, stress, or fungal overgrowth. Treatment often involves using medicated shampoos, creams, or lotions containing antifungal agents or corticosteroids to manage symptoms and control inflammation.
Autoimmune Skin Disorders
Autoimmune skin disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to various skin symptoms. Two autoimmune skin disorders are systemic lupus erythematosus and dermatomyositis.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs, including the skin. Skin manifestations of SLE may include a butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose, as well as other skin changes such as photosensitivity, discoid lesions, and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Treatment for SLE typically involves medications to manage symptoms and control the underlying autoimmune response.
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the muscles and skin. Skin changes associated with dermatomyositis include a violaceous rash on the face, chest, and other sun-exposed areas, as well as characteristic changes around the nails. Treatment for dermatomyositis usually involves medications to control inflammation and suppress the immune system, along with physical therapy to manage muscle weakness.
Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections can affect the skin, leading to various symptoms and discomfort. Two parasitic infections that can mimic skin conditions like scabies are cutaneous larva migrans and myiasis.
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans, also known as “creeping eruption,” is a skin condition caused by the larvae of certain parasites, such as hookworms or strongyloides. The infestation results in red, raised tracks on the skin, which may be intensely itchy and can appear to move as the larvae migrate. Treatment usually involves topical or oral antiparasitic medications to kill the larvae and alleviate symptoms.
Myiasis
Myiasis occurs when fly larvae infest the skin or other body tissues. The larvae feed on living or necrotic tissue, leading to the formation of skin lesions and potential infections. Myiasis can present with a range of symptoms depending on the type of fly larvae involved and the affected area of the body. Treatment typically involves removing the larvae from the skin and addressing any resulting infections.
In conclusion, there are various skin conditions that can mimic the symptoms of scabies or cause similar discomfort. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Proper identification and management of these conditions can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and ensure optimal skin health.