So you’re experiencing a persistent itch that just won’t quit, and you find yourself wondering if it could possibly be scabies. Well, worry not, because this article is here to shed some light on that very question. By exploring the telltale signs and symptoms, as well as the common areas where scabies tend to make their presence known, you’ll soon have the knowledge you need to determine whether or not those dreaded little mites are the cause of your itchiness. Get ready to bid farewell to the uncertainty and say hello to clarity!
Visible Symptoms
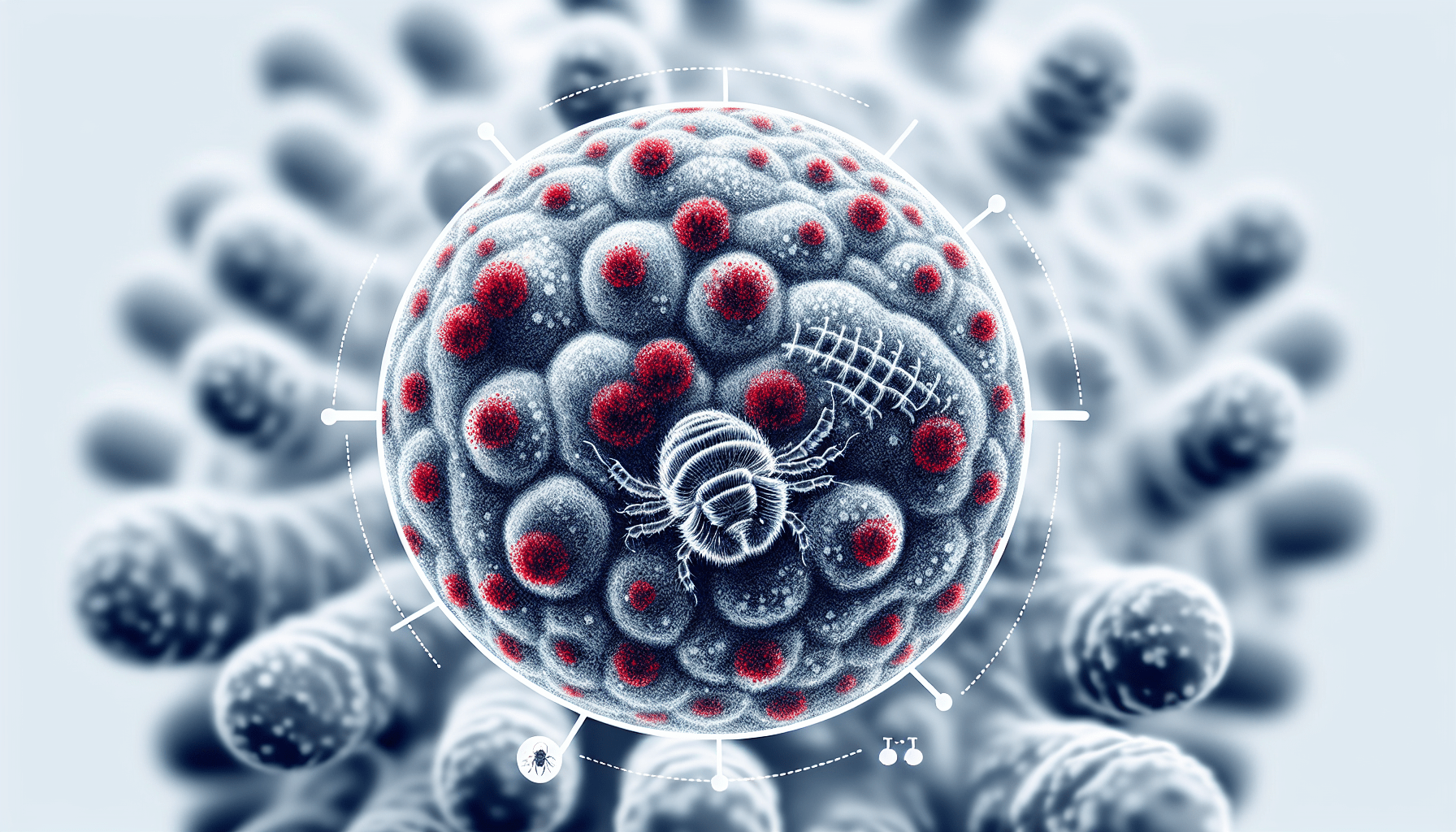
Scabies is a skin condition that can cause several visible symptoms. One of the most common signs of scabies is a rash. The rash typically appears as small, red bumps that may resemble pimples or mosquito bites. It can be itchy and may become more noticeable as the infestation progresses.
Another visible symptom of scabies is the presence of burrows. Burrows are small, thread-like lines that are created by the mites tunneling under the skin. They may appear as tiny raised lines and are often found in the folds of the skin, such as between the fingers, wrists, and elbows.
In some cases, scabies can also lead to the development of blisters on the skin. These blisters are usually filled with fluid and can be quite uncomfortable. They may appear in areas where the infestation is severe or where the skin has been scratched excessively.
Intense Itching
One of the most characteristic symptoms of scabies is intense itching. The itching is often severe and can be worse at night. This can be incredibly distressing and may interfere with your sleep and overall quality of life.
The persistent itch is a result of the mites burrowing into the skin and laying eggs. The human immune system responds to the presence of these mites by releasing histamines, which leads to itching. Scratching the affected areas can provide temporary relief but can also cause further skin damage and introduce bacteria, leading to secondary infections.
Nighttime itch is another common feature of scabies. It may be attributed to the rise in body temperature and increased blood flow to the skin during the night, which can trigger intense itching. This nocturnal itching can further disrupt your sleep and exacerbate the discomfort caused by scabies.
Affected Areas
Scabies can affect various areas of the body, though it tends to prefer warm and moist areas. Some of the most commonly affected areas include between the fingers, where the mites often burrow and create the characteristic linear lines.
The wrists, elbows, and armpits are also common sites for scabies infestations. The folds of the skin in these areas provide the ideal environment for the mites to thrive and reproduce.
Scabies can also occur around the waistline, genitals, and buttocks. These areas offer optimal conditions for the mites to burrow and lay eggs, leading to the development of the characteristic symptoms.
In some cases, scabies can affect the nipples, areolas, and breasts, particularly in women. This can often be a source of great discomfort and may require specific attention and treatment.
Lastly, scabies can also appear on the feet and toes. The warm and moist environment created by wearing socks and closed-toe shoes provides an ideal breeding ground for the mites.
Close Contact with Infected Person
Scabies is highly contagious and can easily spread through close contact with an infected person. There are several ways in which scabies can be transmitted.
Sharing personal items with an infected individual is a common mode of transmission. Items such as clothing, towels, bedding, and even personal care items like brushes or combs can harbor the mites and their eggs. Coming into contact with these items can lead to the transfer of the scabies mites onto your own skin.
Sexual contact can also transmit scabies. The mites can easily spread during intimate activities such as sexual intercourse, resulting in an infestation of the genital and surrounding areas.
Living in crowded spaces, such as nursing homes, schools, or dormitories, can increase the risk of scabies transmission. The close proximity between individuals in these environments allows for easy transfer of the mites from one person to another.
Incubation Period
After coming into contact with scabies, it can take anywhere from 2 to 6 weeks for symptoms to appear. This period is known as the incubation period. During this time, the mites are reproducing and laying eggs under your skin, but you may not experience any symptoms yet.
It is important to note that even if you are not experiencing any symptoms during the incubation period, you can still spread scabies to others. Therefore, it is crucial to take precautions and seek medical attention if you suspect you have been exposed to scabies.
Medical Diagnosis
To diagnose scabies, a medical professional will typically perform a physical examination to assess the visible symptoms. They will closely inspect the affected areas of your skin for signs of the characteristic rash, burrows, or blisters.
In some cases, the doctor may perform a skin scraping. This involves gently scraping the surface of your skin to collect a sample of the affected skin cells. The sample is then examined under a microscope to look for the presence of scabies mites, their eggs, or feces.
Microscopic examination is another method used to diagnose scabies. A small piece of the affected skin is removed and placed under a microscope to identify the mites or their eggs.
Other Symptoms
In addition to the visible symptoms and intense itching, scabies can sometimes cause other accompanying symptoms. One such symptom is a fever. Though not a common symptom, some individuals with scabies may experience a mild fever, which is thought to be a result of the body’s immune response to the infestation.
Another possible symptom of scabies is swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that are part of the immune system. When the body is fighting off an infection or infestation, the lymph nodes near the affected area can become swollen and tender to the touch.
Exclusion of Other Conditions
It is important to note that scabies can sometimes be mistaken for other skin infections or conditions. To properly diagnose scabies, a doctor must distinguish it from these other possibilities.
Distinguishing scabies from other skin infections may involve a careful evaluation of the visible symptoms, a review of the medical history, and consideration of any potential exposure to scabies.
The ability to accurately diagnose scabies is crucial, as it allows for the appropriate treatment to be administered, minimizing the discomfort and preventing the further spread of the infestation.
Children and Infants
Scabies can affect individuals of all ages, including children and infants. In fact, scabies is quite common among children, particularly in childcare settings where close interactions are frequent.
Common signs of scabies in children include the same visible symptoms seen in adults, such as the characteristic rash, burrows, and blisters. However, children may not communicate their discomfort or itching as effectively as adults, making it important for parents and caregivers to be vigilant.
In childcare settings, scabies can spread easily among children due to their close interactions and shared items. It is crucial for parents, caregivers, and childcare professionals to be aware of the signs and symptoms of scabies and take appropriate measures to prevent its spread.
Seeking Medical Advice
If you suspect you may have scabies, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. A healthcare professional can provide you with the necessary guidance and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Professional guidance is essential in accurately diagnosing scabies and ruling out other conditions that may present with similar symptoms. A medical professional will be able to perform a thorough examination, ask pertinent questions, and determine the best course of action based on your specific circumstances.
Avoid self-diagnosis when it comes to scabies. While it may be tempting to rely on internet resources or self-treatment methods, scabies is a serious condition that requires proper medical attention. Self-treatment can lead to delays in obtaining effective treatment and increase the risk of complications and further spread of the infestation.
In conclusion, if you notice visible symptoms such as rash, burrows, or blisters, experience intense itching, or have been in close contact with an infected person, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Remember, scabies is highly contagious and can easily spread, so early detection and appropriate treatment are key in managing the condition effectively.