Scabies, a common skin condition that causes intense itching and a rash, has long been associated with poor hygiene and being dirty. However, is there any truth to this belief? In this article, we will explore the connection between scabies and personal hygiene, and whether being dirty truly increases the risk of contracting this contagious ailment. So, let’s debunk the myths and get to the bottom of this itchy matter!
Understanding Scabies
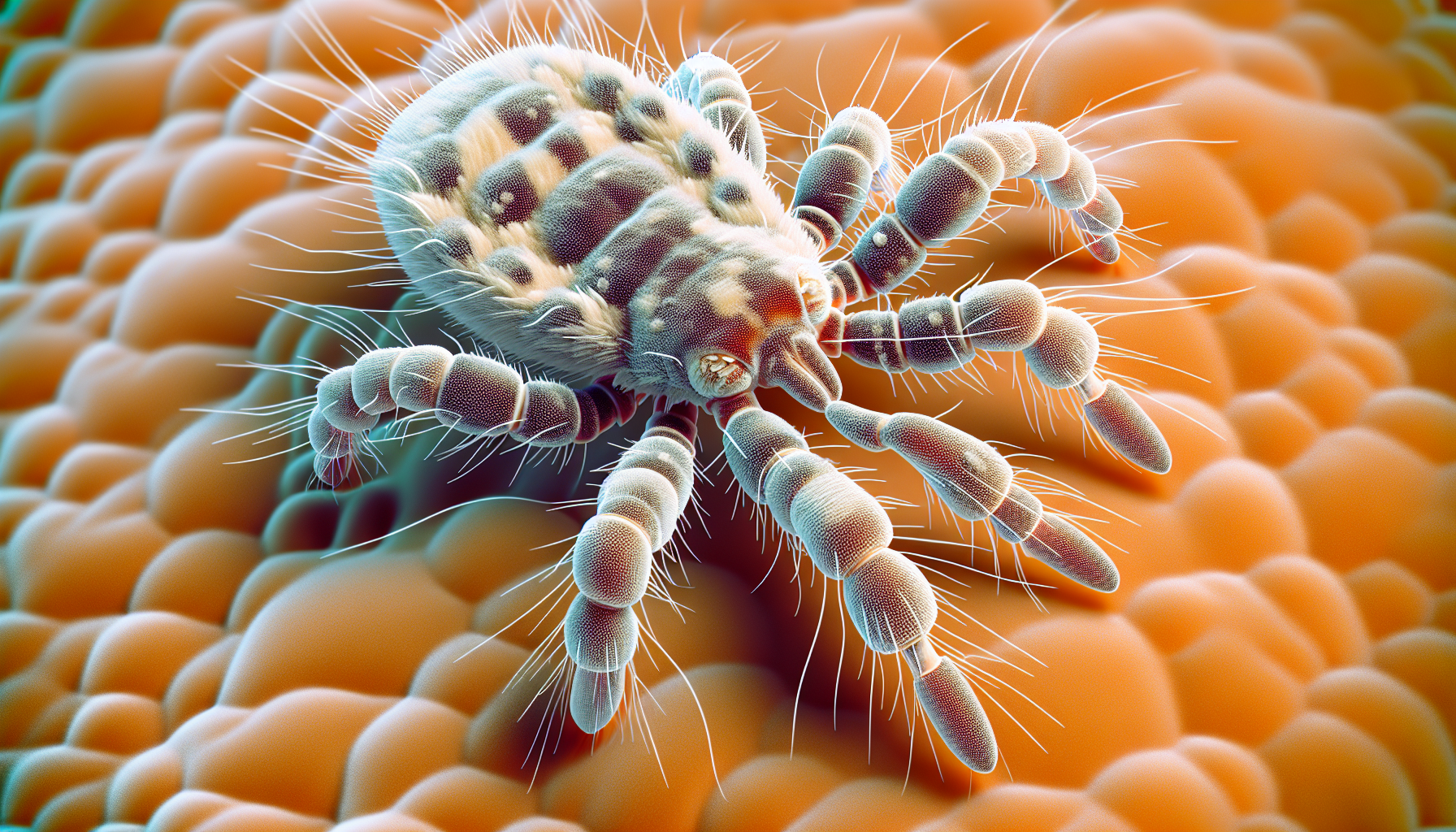
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. This microscopic creature burrows into the top layer of your skin, causing intense itching and a red rash. It is important to have a good understanding of this condition in order to prevent its spread and seek appropriate treatment.
What is scabies?
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The female mites burrow into the skin and lay eggs, which then hatch and grow into new mites. This infestation leads to the characteristic symptoms of scabies, such as intense itching, especially at night, and a pimple-like rash.
How is scabies spread?
Scabies is primarily spread through close physical contact with an infected individual. This can include prolonged skin-to-skin contact, such as holding hands, sexual activity, or even sharing bedding and clothes. It is also possible to contract scabies by touching contaminated surfaces, although this is less common.
Common symptoms of scabies
The most common symptom of scabies is intense itching, which can be particularly bothersome at night. This itching is often accompanied by a rash, which consists of small red bumps or blisters. The rash typically appears in areas where the mites have burrowed, such as between the fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, and genitals. In infants and young children, the rash may also be present on the head, face, neck, and soles of the feet.
Causes of Scabies
The mite Sarcoptes scabiei
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, an eight-legged arthropod that is barely visible to the naked eye. The female mites burrow into the top layer of the skin and lay eggs, which hatch and develop into new mites. This ongoing cycle of infestation leads to the symptoms of scabies.
Transmission through close physical contact
Scabies is highly contagious and can be easily transmitted through close physical contact with an infected person. The mites can transfer from one person to another during activities such as shaking hands, hugging, or engaging in sexual intercourse. It is important to be cautious and practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of scabies.
Risk factors for scabies
Certain factors can increase your risk of contracting scabies. Living in close quarters with infected individuals, such as within households or nursing homes, significantly raises the likelihood of transmission. Additionally, being in crowded and unsanitary environments, such as homeless shelters or refugee camps, increases the risk of scabies infestations.
Dispelling the Myth
Scabies can affect anyone
Contrary to popular belief, scabies can affect people from all walks of life and is not exclusive to those who are perceived as “dirty”. It is important to understand that scabies is not a reflection of personal hygiene or cleanliness. Anyone can contract scabies, regardless of their socioeconomic status or living conditions.
Scabies is not a result of poor hygiene
Scabies is caused by the infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite and is not related to poor hygiene. The mites do not differentiate between clean or dirty skin when searching for a new host. It is essential to dispel this misconception in order to promote a better understanding of the condition and reduce the stigma associated with it.
Risk Factors for Scabies
Shared living spaces
Living in close proximity with individuals who have scabies significantly increases the risk of contracting the condition. This includes sharing a household, dormitory, or any other living arrangement where physical contact is frequent. It is crucial to address scabies infestations promptly in such settings to prevent its spread.
Close contact environments
Environments that entail close physical contact, such as schools, daycares, and healthcare facilities, pose a higher risk of scabies transmission. The ease with which mites can be passed on through direct skin-to-skin contact in these settings makes preventive measures and early detection vital to controlling outbreaks.
Crowded and unsanitary conditions
Crowded and unsanitary conditions provide an ideal breeding ground for scabies mites. This includes places like refugee camps, prisons, and homeless shelters. The close quarters and lack of proper hygiene practices can facilitate the rapid spread of scabies. Therefore, it is crucial to address these environmental factors to prevent and control infestations.
Prevention of Scabies
Maintaining personal hygiene
While personal hygiene is not a direct cause of scabies, practicing good hygiene can help reduce the risk of infestation. Regularly washing your hands and body with soap and water can help minimize the chances of mites transferring onto your skin. It is also essential to keep your nails clean and trimmed to prevent the possibility of scratching and causing further irritation.
Avoiding direct skin contact
Avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals can significantly lower the risk of scabies transmission. This includes refraining from hugging, kissing, or sharing personal items, such as clothing, bedding, and towels. Maintaining a safe distance from known cases of scabies can help prevent its spread.
Washing and disinfecting clothing and bedding
Regularly washing and disinfecting clothing, bedding, and other personal items is crucial in preventing the spread of scabies. Using hot water and a suitable detergent can effectively kill any mites or eggs present on the fabrics. Additionally, drying the items on high heat can further aid in eliminating the mites.
Treatment for Scabies
Prescription topical creams and ointments
Topical creams and ointments prescribed by healthcare professionals are the most common form of treatment for scabies. These medications, such as permethrin and ivermectin, are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin. It is important to follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the eradication of the mites.
Oral medications
In more severe cases or when topical treatments are not effective, oral medications may be prescribed. These medications, such as ivermectin, work by killing the scabies mites throughout the body. Oral medications are often used in conjunction with topical treatments to ensure thorough eradication of the infestation.
Cleaning and disinfecting the environment
In addition to treating the affected individual, it is crucial to thoroughly clean and disinfect their living environment. This includes washing bedding, clothing, and personal items in hot water, vacuuming furniture and carpets, and ensuring proper sanitation practices. This comprehensive approach helps prevent re-infestation and reduces the risk of spreading scabies to others.
Complications of Scabies
Secondary skin infections
Uncontrolled scratching due to intense itching can create breaks in the skin, making it vulnerable to secondary bacterial infections. These infections can further exacerbate the symptoms of scabies and may require additional medical intervention, such as antibiotics. It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you notice signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
Post-scabies syndrome
In some cases, even after successful treatment, individuals may experience lingering symptoms known as post-scabies syndrome. This can include prolonged itching and skin irritation, which may persist for weeks or months following the eradication of the mites. If you continue to experience symptoms after treatment, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
When to Seek Medical Help
Persistent itching and rash
If you experience persistent itching and the appearance of a rash that lasts for more than a few days, it is important to seek medical help. These symptoms may be indicative of scabies or another skin condition, and an accurate diagnosis is necessary for appropriate treatment.
Symptoms worsen or spread
If your symptoms worsen or spread to new areas of your body despite following treatment guidelines, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. This could indicate a treatment-resistant infestation or other underlying factors contributing to the persistence of symptoms.
Signs of secondary infection
If you notice signs of a secondary infection, such as increased redness, swelling, pain, or discharge from the affected areas, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. Secondary infections can complicate the treatment and management of scabies and may require additional intervention.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to understand that scabies is not a result of poor hygiene and can affect anyone. It is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite and primarily spreads through close physical contact. By taking preventive measures, such as practicing good personal hygiene, avoiding direct skin contact, and washing and disinfecting clothing and bedding, the risk of contracting scabies can be minimized. Timely treatment with prescription medications, coupled with thorough cleaning and disinfection of the environment, is essential for effectively combating scabies infestations. Remember, seeking medical help when needed and dispelling myths associated with scabies are important steps in managing and controlling this condition. With proper understanding and adherence to prevention and treatment measures, scabies can be effectively managed and controlled.