Imagine you’re living your best, squeaky clean life, taking all the necessary precautions to maintain your hygiene. But then, out of nowhere, the itchiness begins. Yes, you read that correctly – scabies, the tiny mites that can afflict even the cleanest of individuals. In this article, we will explore the puzzling question of how a spotless person can end up with scabies, uncovering the surprising truths behind this unexpected infestation. Get ready to uncover the mystery behind scabies and learn how to protect yourself, because even the cleanest are not immune.
What is Scabies?
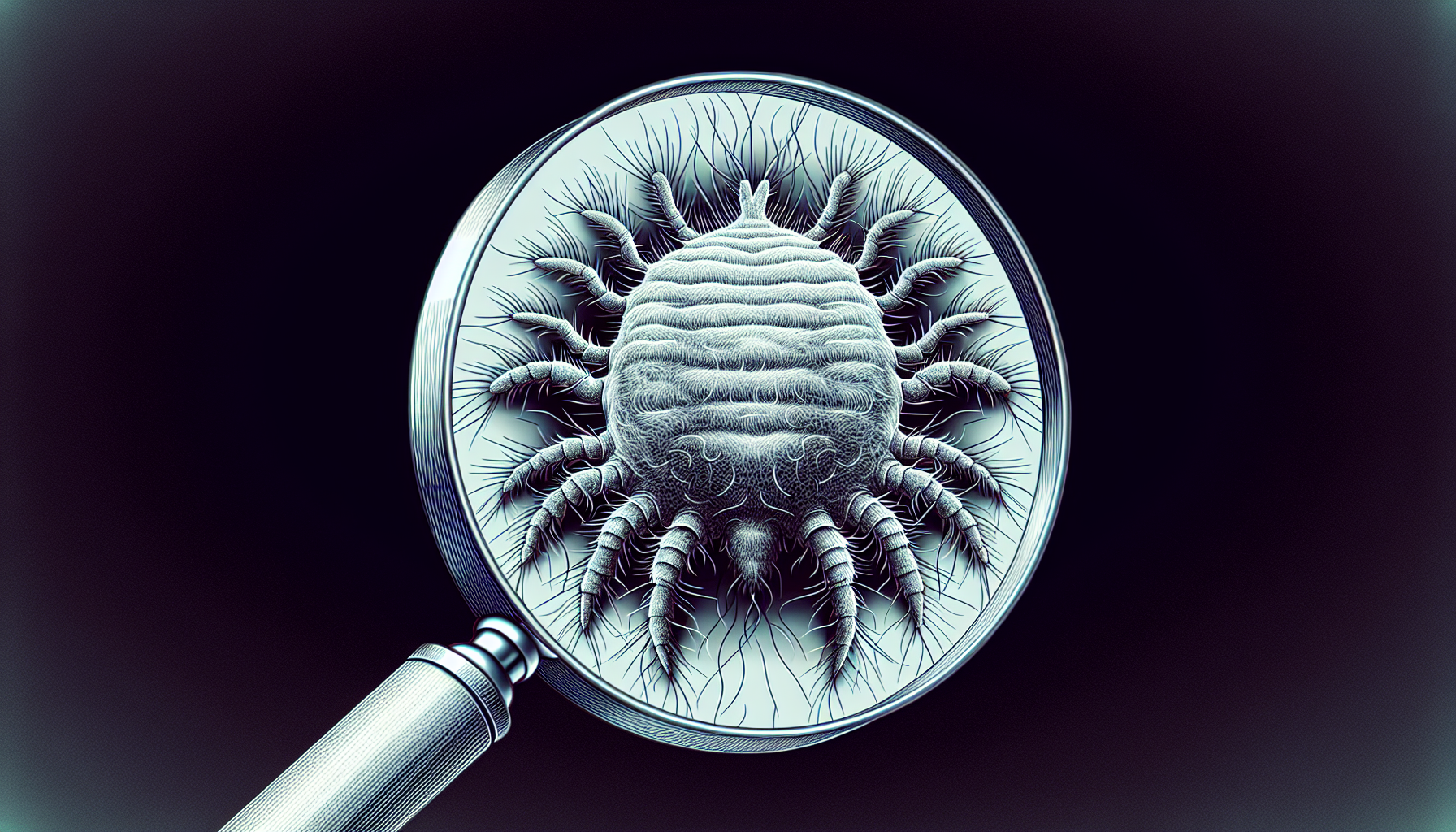
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the infestation of the human itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching and a rash with small burrows on the skin. Scabies can affect anyone, regardless of their level of cleanliness or personal hygiene.
Definition
Scabies is a parasitic infestation that occurs when the female itch mite burrows into the skin to lay eggs. The mites then multiply, leading to an allergic reaction in the form of a rash and intense itching.
Causes
Scabies is caused by direct or indirect contact with an infected person or by sharing personal items with someone who has scabies. The mites can survive for up to 48-72 hours off the human body, allowing them to spread through indirect contact.
Symptoms
The common symptoms of scabies include intense itching, especially at night, and a pimple-like rash. The rash may consist of small, raised, grayish-white or skin-colored bumps, often with irregular lines. The itching is the result of a hypersensitivity reaction to the mites’ enzymes and waste products.
Transmission of Scabies
Direct Skin-to-Skin Contact
Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person is the most common way scabies is transmitted. This can occur during activities such as hugging, holding hands, or sexual contact. It is important to note that scabies mites cannot jump or fly, so prolonged skin contact is required for transmission.
Indirect Contact
Scabies can also be transmitted through indirect contact with infested items, such as clothing, bedding, or furniture. The mites can survive outside the body for a limited time, increasing the risk of transmission through contact with contaminated surfaces.
Sharing Personal Items
Sharing personal items, such as clothing, towels, or bedding, with an infected person can lead to scabies transmission. The mites can easily transfer from one person to another through these items, especially if they are not properly cleaned or disinfected.
Myths vs Facts about Scabies
Scabies only affects dirty people
Contrary to popular belief, scabies does not only affect dirty or unhygienic individuals. It is a common misconception that scabies is a result of poor personal hygiene. Scabies can infect anyone, regardless of their level of cleanliness, as it is primarily transmitted through direct or indirect skin contact.
Scabies is caused by poor hygiene
Another myth about scabies is that it is caused by poor hygiene. While maintaining good personal hygiene is essential for overall health, scabies is caused by the human itch mite and its transmission methods, not by lack of cleanliness.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Getting Scabies
Living in crowded environments
Living in crowded environments, such as dormitories, nursing homes, or military barracks, can increase the risk of scabies transmission. Close quarters and frequent physical contact make it easier for the mites to spread from person to person.
Being in close contact with an infected person
Being in close contact with an infected person, whether through family members, friends, or intimate partners, significantly increases the risk of contracting scabies. Sharing the same living space or engaging in prolonged skin contact can facilitate the transmission of the mites.
Having a weakened immune system
Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, undergoing chemotherapy, or taking immunosuppressive medications, are more susceptible to scabies infestation. A compromised immune system reduces the body’s ability to fight off the mites, leading to a higher risk of infection.
The Role of Cleanliness in Scabies Prevention
Importance of personal hygiene
While scabies can infect anyone, maintaining good personal hygiene can help minimize the risk of transmission. Regularly washing your hands with soap and water, keeping your body clean, and practicing proper skincare can contribute to overall well-being and reduce the chances of scabies infestation.
Cleaning and disinfecting personal items
To prevent scabies transmission, it is crucial to clean and disinfect personal items regularly. Clothing, towels, bedding, and other items that come into contact with the skin should be washed in hot water and dried on high heat. If unable to launder, sealing items in a plastic bag for several days can kill the mites.
Maintaining a clean living environment
Maintaining a clean living environment is essential in preventing scabies outbreaks. Regularly vacuuming furniture, disinfecting surfaces, and ensuring proper hygiene practices among household members can help eliminate mites and prevent their spread.
Uncommon Ways of Contracting Scabies
Contaminated bedding or furniture
Scabies mites can survive for a limited time on bedding or furniture, making it possible to contract scabies through contact with contaminated items. While less common than direct skin-to-skin contact, it is still important to take necessary precautions when using shared bedding or furniture.
Healthcare-related transmission
In rare cases, scabies can be contracted in healthcare settings, such as hospitals or nursing homes. Healthcare-related transmission of scabies can occur due to close contact with infected individuals, inadequate hygiene practices, or overcrowded conditions. Strict infection control measures and proper hygiene protocols are necessary to minimize the risk.
Scabies Outbreaks in Clean Environments
Schools and childcare centers
Scabies outbreaks can occur even in clean and hygienic environments, such as schools and childcare centers. The close proximity and frequent physical contact among children provide an opportunity for scabies transmission. Prompt identification and treatment of infected individuals, along with thorough cleaning and disinfection, are crucial in preventing outbreaks.
Nursing homes and long-term care facilities
Nursing homes and long-term care facilities are susceptible to scabies outbreaks due to the vulnerable population they serve. Close living quarters and compromised immune systems make residents more susceptible to scabies infestation. Regular monitoring, early detection, and effective treatment are essential in managing outbreaks in these settings.
Diagnosing Scabies in Clean Individuals
Visual examination
A visual examination by a healthcare professional is the first step in diagnosing scabies. The characteristic rash, along with the presence of burrows, can help healthcare providers identify scabies infestation.
Skin scrapings
Skin scrapings may be taken to confirm the presence of scabies mites or their eggs. A microscope is used to examine the skin samples for the presence of mites, mite eggs, or fecal matter.
Dermoscopy
Dermoscopy, also known as skin surface microscopy, can be used to examine the skin more closely and identify the characteristic signs of scabies. It involves using a handheld device with a magnifying lens to visualize the skin and identify the mites or their burrows.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Topical medications
Topical medications, such as creams or lotions, are the primary treatment for scabies. These medications, usually containing permethrin or sulfur, are applied to the entire body from the neck down and left on for a specified period. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and complete the full course of treatment.
Oral medications
In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to treat scabies. These medications, such as ivermectin, work by killing the mites from within the body. Oral medications are often used when topical treatments have been ineffective or when the infestation is severe.
Treating close contacts
Close contacts of an infected individual, even if they do not show symptoms, should also be treated to prevent further transmission. Treating all individuals who have had prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person is essential in preventing recurrent infestations and spreading the mites to others.
Preventing Scabies Transmission
Isolation of infected individuals
Isolating infected individuals during the initial stages of treatment can help prevent the spread of scabies to others. By minimizing direct skin-to-skin contact and ensuring proper hygiene practices, the risk of transmission can be significantly reduced.
Proper hygiene practices
Practicing proper hygiene, such as regular handwashing, helps prevent scabies transmission. It is essential to wash hands thoroughly with soap and water, particularly after coming into contact with an infected individual or contaminated items.
Avoiding close contact with infected persons
Avoiding close contact with infected persons, especially during the treatment period, is crucial in preventing scabies transmission. While it may be difficult to completely avoid contact with family members or intimate partners, minimizing prolonged skin contact can help reduce the risk of infestation.