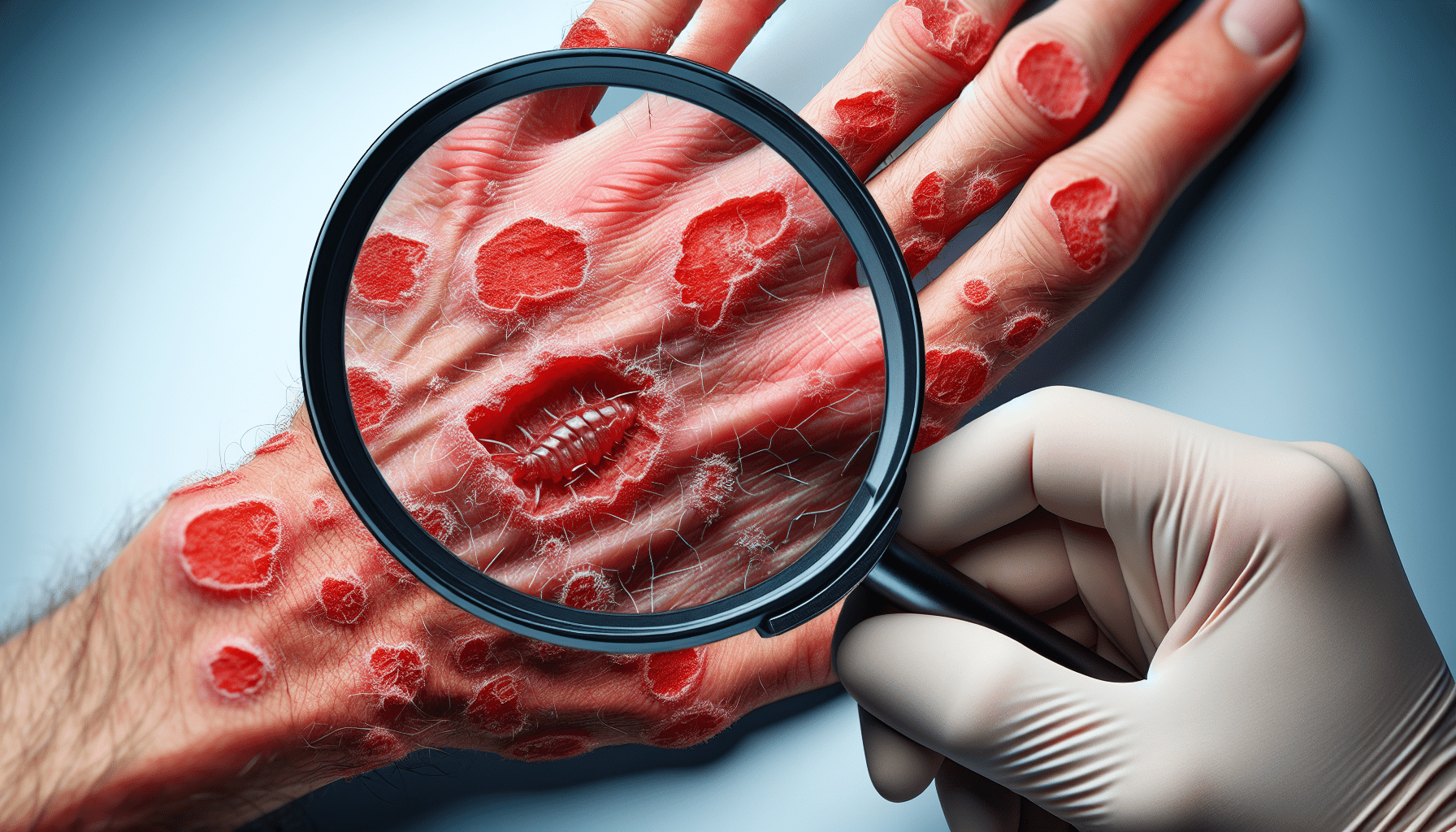
Have you ever experienced itching and rashes on your skin, but were unsure whether it was scabies or a fungal infection? It’s not always easy to distinguish between the two, but being able to identify the differences is crucial in order to receive the appropriate treatment. In this article, we will explore the distinct characteristics of scabies and fungal infections, allowing you to confidently differentiate between the two and seek the right course of action for your skin condition. So, let’s dive right in and unravel the mystery behind scabies and fungal infections!
Overview
Scabies and fungal infections are two common skin conditions that can cause discomfort and irritation. While they may share some similarities, it’s important to understand the differences between them in order to seek the appropriate treatment. This article will provide an overview of scabies and fungal infections, including their causes, symptoms, affected areas, transmission, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, complications, and when to seek medical help.
Understanding Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by tiny mites called Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow into the skin, laying eggs and causing intense itching. Scabies is commonly spread through close contact with an infected person, and it often occurs in crowded environments such as nursing homes or schools. The most common symptom of scabies is severe itching, especially at night. Other symptoms may include a rash, blisters, and the presence of burrows on the skin. It’s important to note that scabies can affect any part of the body, including the palms, between the fingers, and the genital area.
Understanding Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by various types of fungi that thrive in warm and moist environments. These infections can affect different parts of the body, including the skin, nails, and hair. Fungal infections are usually not contagious and can be caused by different types of fungi, such as dermatophytes, yeasts, or molds. The symptoms of fungal infections can vary depending on the affected area, but common signs may include redness, itching, peeling skin, and the presence of a rash. Some of the most common types of fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
Causes of Scabies
Scabies is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which is transmitted through close contact with an infected individual. The mites can easily spread from person to person through skin-to-skin contact, prolonged contact with infested clothing or bedding, or even through sexual contact. Sharing personal items with an infected person, such as towels or bedding, can also contribute to the spread of scabies. It’s important to note that scabies can affect people of all ages and socioeconomic backgrounds, and it is not necessarily an indication of poor hygiene.
Causes of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are caused by various types of fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and molds. These fungi can be found in the environment, such as soil, plants, and even on the skin of humans and animals. Fungal infections are more likely to occur in warm and moist environments, as these conditions promote fungal growth. Factors such as weakened immune system, poor hygiene, prolonged use of antibiotics, and wearing tight or non-breathable clothing can also increase the risk of developing a fungal infection. It’s important to note that fungal infections are not contagious in most cases, with the exception of certain types like ringworm.
Symptoms of Scabies
The most common symptom of scabies is intense itching, which is often worse at night. This itching is a result of the body’s reaction to the mites and their waste products. In addition to the itching, scabies may also cause a rash, blisters, or pimple-like bumps on the skin. These skin changes are typically found in the areas where the mites have burrowed, such as between the fingers, on the wrists, elbows, armpits, buttocks, and genital area. It’s important to note that scabies can affect people differently, and some individuals may experience symptoms that are less typical, such as scalp involvement or minimal itching.
Symptoms of Fungal Infections
The symptoms of fungal infections can vary depending on the type and location of the infection. However, common signs include redness, itching, peeling or scaling of the skin, and the presence of a rash. For example, athlete’s foot often presents as redness, itchiness, and a scaly rash between the toes. On the other hand, ringworm can cause a circular, red rash with raised edges and a clear center. Fungal infections of the nails, known as onychomycosis, can lead to thickened, crumbly, or discolored nails. In some cases, fungal infections may also cause hair loss or a burning sensation on the affected area.
Commonly Affected Areas in Scabies
Scabies can affect any part of the body, but certain areas are more commonly affected. The mites tend to burrow in areas where the skin is thin or folds, allowing them to easily penetrate the skin. Commonly affected areas in scabies include the spaces between the fingers, on the wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, buttocks, and the genital area. In infants and young children, scabies may also affect the scalp and face. It’s important to note that scabies can spread rapidly, so it’s crucial to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent further transmission.
Commonly Affected Areas in Fungal Infections
The areas commonly affected by fungal infections depend on the specific type of infection. For example, athlete’s foot typically affects the skin between the toes, while ringworm commonly affects the scalp, feet, groin, and other areas of the body. Fungal infections of the nails, known as onychomycosis, usually affect the toenails or fingernails. Fungal infections can also occur on other parts of the body, such as the hands, torso, and even in the mouth. It’s important to note that the presence of a moist or warm environment can increase the risk of fungal growth and subsequent infection.
Transmission of Scabies
Scabies is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person through close and prolonged contact. The mites can rapidly move from one person to another during activities such as hugging, sexual contact, or sharing items like clothing or bedding. Scabies can also be transmitted indirectly through contact with infested surfaces, such as furniture or towels. It’s worth mentioning that scabies mites can survive outside the human body for a short period of time, so it’s important to wash or dry-clean infested clothing and bedding to prevent reinfestation.
Transmission of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are typically not contagious from person to person. However, they can be transmitted indirectly through contact with infected surfaces or objects, such as public showers, swimming pools, or shared personal items like towels or clothing. The fungi responsible for these infections can thrive in warm and moist environments, making it important to maintain good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items in order to prevent transmission. Certain types of fungi, such as those causing ringworm or yeast infections, may be contagious and can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact.
Diagnostic Methods for Scabies
To diagnose scabies, a healthcare professional will generally start with a physical examination of the affected area. They may look for characteristic signs of scabies, such as burrows or rash patterns. To confirm the diagnosis, they may perform a skin scraping or biopsy to examine the skin under a microscope or through other laboratory tests. Additionally, in some cases, a dermatologist may use a dermoscope, a handheld device that provides magnified views of the skin, to aid in the diagnosis.
Diagnostic Methods for Fungal Infections
The diagnosis of fungal infections typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare professional may visually inspect the affected area and ask about any symptoms or exposure to potential sources of infection. To confirm the diagnosis, they may collect a sample of skin, hair, or nails for analysis. This sample is usually sent to a laboratory to identify the type of fungi causing the infection. In some cases, a microscopic examination or culture of the sample may be necessary to determine the specific fungal species.
Treatment Options for Scabies
Scabies is usually treated with medications that kill the mites and their eggs. The most common treatment is a prescription cream or lotion that contains insecticides, such as permethrin or ivermectin. These medications are applied to the entire body from the neck down and left on for a specified period of time. In some cases, oral medications may be prescribed to treat severe or resistant cases of scabies. It’s crucial to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and to treat all close contacts to prevent reinfestation.
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections
The treatment of fungal infections depends on the specific type and severity of the infection. Mild cases of fungal infections can often be treated with over-the-counter antifungal creams, powders, or sprays. These medications are usually applied directly to the affected area and may need to be used for several weeks until the infection clears. More severe or persistent fungal infections may require prescription-strength antifungal medications, either in topical or oral form. It’s important to carefully follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and to complete the full course of treatment to ensure eradication of the infection.
Preventing Scabies
To prevent scabies, it’s important to avoid close contact with infected individuals and to practice good hygiene. If you come into contact with someone who has scabies, it’s advisable to wash your clothing and bedding in hot water and dry them on high heat. Personal items that cannot be washed, such as stuffed toys or certain furniture, can be sealed in a plastic bag for several days to kill any mites. Avoid sharing personal items, such as towels, clothing, or bedding, with others to minimize the risk of transmission. If you suspect you have been exposed to scabies, it’s important to seek medical help promptly to prevent the spread of the infestation.
Preventing Fungal Infections
To prevent fungal infections, it’s important to practice good hygiene and maintain a clean and dry environment. Keep your skin clean and dry, paying particular attention to areas that tend to perspire, such as the armpits and groin. Avoid wearing tight or non-breathable clothing, as this can create a warm and moist environment ideal for fungal growth. Change your socks and shoes regularly, especially after exercising or sweating. It’s also important to avoid walking barefoot in public areas, such as public showers or swimming pools, to reduce the risk of acquiring a fungal infection.
Complications of Scabies
While scabies is generally a self-limiting condition, complications can arise if left untreated or if there are underlying medical conditions. Scratching the itchy skin can lead to secondary skin infections, such as impetigo or cellulitis. In severe cases, scabies can cause a condition called crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, which is characterized by a thick crust of skin containing large numbers of mites. Crusted scabies is more contagious and difficult to treat than typical scabies, often requiring multiple rounds of medications and extensive hygiene measures.
Complications of Fungal Infections
If left untreated, fungal infections can persist or spread to other areas of the body. In severe cases, fungal infections can lead to complications such as cellulitis, abscess formation, or the development of chronic or recurrent infections. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing cancer treatments, are particularly susceptible to severe fungal infections. It’s important to seek treatment for fungal infections promptly to prevent the progression of the infection and minimize the risk of complications.
When Should You Seek Medical Help for Scabies?
If you suspect you have scabies, it’s advisable to seek medical help as soon as possible. A healthcare professional can provide a definitive diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. It’s especially important to seek medical attention if you experience intense itching that disrupts your daily activities or if the itching persists after self-treatment. Additionally, if you notice any signs of secondary skin infections, such as increased pain, redness, swelling, or the formation of pus, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
When Should You Seek Medical Help for Fungal Infections?
If you suspect you have a fungal infection and over-the-counter treatments have not provided relief within a reasonable timeframe, it’s recommended to seek medical help. A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the type of fungal infection and prescribe the appropriate treatment. It’s particularly important to seek medical attention if the infection is severe, persistent, or affects sensitive areas such as the face, scalp, or genitals. Additionally, individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying medical conditions should consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management of fungal infections.