Welcome to the myth-busting article on scabies! Many people believe that not washing regularly can lead to scabies, but the truth is that this common skin infestation is actually caused by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. While cleanliness is important for overall health, scabies is not a result of poor hygiene. Let’s dive into the facts behind this misunderstood condition and learn how to effectively treat and prevent it.
Is Scabies Caused By Not Washing?
Have you ever wondered if scabies, a skin infestation caused by mites, is the result of not washing your clothes or yourself regularly? In this article, we will explore the causes of scabies and dispel common myths surrounding this contagious skin condition. Let’s dive in and learn more about scabies and how you can prevent and treat it.
What Is Scabies?
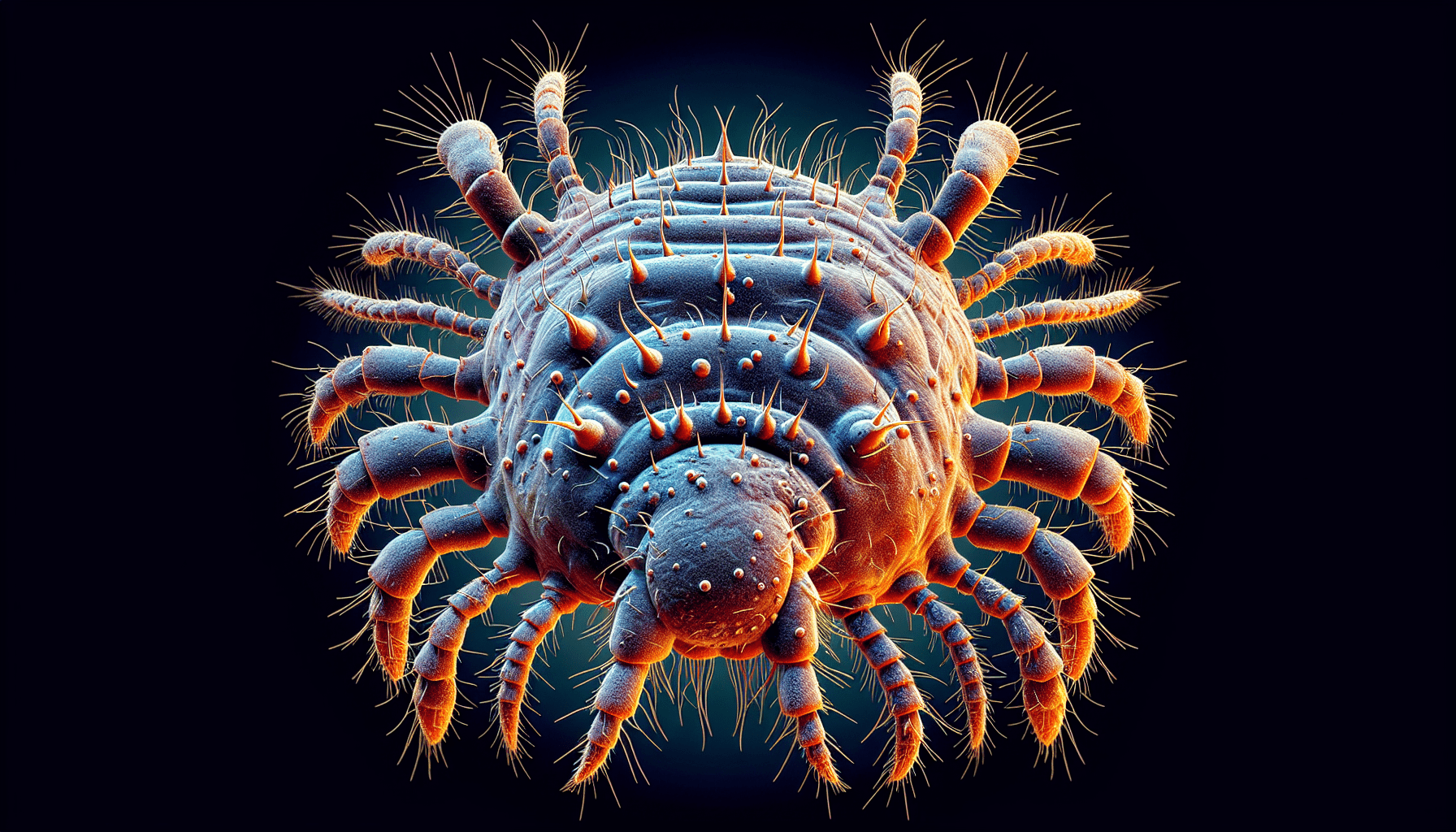
Scabies is an itchy skin condition caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. These mites burrow into the upper layer of your skin, where they lay eggs and cause an allergic reaction that results in intense itching. Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through close physical contact with an infected person.
So now you know what scabies is, but let’s address the burning question: is it really caused by not washing regularly?
Debunking The Myth: Scabies And Personal Hygiene
Contrary to popular belief, scabies is not caused by poor personal hygiene or lack of cleanliness. Scabies mites can infest anyone, regardless of their hygiene practices. In fact, scabies is often spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual, making it possible for even the most hygienic person to contract the infestation.
If you or someone you know has scabies, it’s important to seek treatment promptly to prevent the infestation from spreading to others. However, it’s essential to understand that scabies is not a reflection of your personal hygiene habits.
How Is Scabies Spread?
Scabies is primarily spread through close physical contact with an infected person. This can happen during activities such as hugging, holding hands, or sexual contact. The mites can also spread through sharing personal items like clothing, bedding, or towels with an infected individual.
The infestation can easily spread among family members, close friends, or individuals living in crowded or communal settings. If one person in a household or group has scabies, it’s crucial for everyone else to get checked and treated to prevent the mites from spreading further.
Signs And Symptoms Of Scabies
The symptoms of scabies usually appear 2-6 weeks after infestation, making it challenging to identify the source of the mites. Common signs and symptoms of scabies include:
- Intense itching, especially at night
- A pimple-like rash
- S-shaped or linear burrows on the skin
- Redness and inflammation
- Sores and secondary infections from scratching
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to see a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Scabies
Diagnosing scabies involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider, who may also perform a skin scraping to check for mites, eggs, or fecal matter under a microscope. Once diagnosed, scabies can be treated with topical medications like permethrin or oral medications like ivermectin to kill the mites and relieve symptoms.
In addition to medication, it’s crucial to wash all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water and dry them on high heat to kill any remaining mites. It’s also essential to vacuum carpets and furniture, as well as inform close contacts so they can seek treatment if necessary.
Preventing Scabies Infection
To prevent scabies infection, it’s essential to take certain precautions, especially if you are in close contact with individuals who have scabies. Here are some tips to help you avoid contracting scabies:
- Avoid close physical contact with individuals who have scabies.
- Do not share personal items like clothing, bedding, or towels with anyone who has scabies.
- Wash your hands frequently, especially after touching or treating an infected individual.
- Clean and vacuum your living space regularly to remove any mites that may be present.
- Seek medical treatment promptly if you suspect you have been exposed to scabies.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of contracting scabies and prevent the spread of the infestation to others.
Myth Busted: Scabies And Personal Hygiene
Now that you have a better understanding of scabies and how it spreads, it’s clear that personal hygiene is not the cause of this contagious skin condition. Scabies can affect anyone, regardless of their cleanliness habits, making it crucial to focus on prevention and treatment rather than blame or misconceptions.
If you or someone you know is dealing with scabies, remember that seeking medical attention and following treatment guidelines are essential steps in overcoming this infestation. By taking proper precautions and educating yourself and others about scabies, you can effectively manage the condition and prevent it from spreading further.
In conclusion, scabies is not caused by not washing; it is a parasitic infestation that can happen to anyone. By debunking myths and understanding the facts about scabies, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this common yet misunderstood skin condition.
So the next time you hear someone say that scabies is caused by not washing, you can confidently explain the truth behind this contagious skin condition. Stay informed, stay healthy, and remember that scabies is not a reflection of your personal hygiene practices.